
ORKA

 |
ORKA |
 |
Welcome to ORKA!
ORKA is a rare kaon decay experiment to be performed at Fermilab, using the CDF magnet ( CDF hall ) , with primary beam from the Main Injector operating at 95 GeV. ORKA seeks a high precision measurement (~5%) of the branching ratio for the reaction K+→π+νν which occurs at the level of one in 10 billion decays and is highly sensitive to new physics effects. The experiment will study a rich array of other processes. ORKA employs a low energy stopped kaon beam and builds on the techniques developed by the BNL E949 and E787 experiments which made the initial observations of K+ → π+ ν ν. ORKA is scoped to run for three to five years and obtain a sample of >1000 K+ → π+ ν ν decays.
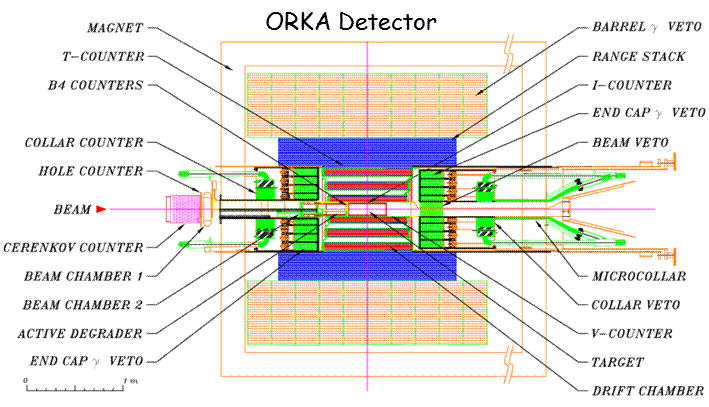 |  |
| ORKA detector schematic diagram | CDF COT removal (the ORKA detector fits within the COT) |
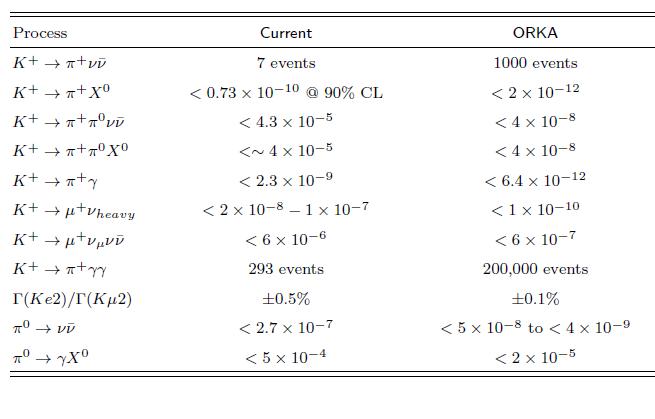
| The table below shows the expected event yields or branching ratio limits to be achieved by a five-year ORKA run compared to current results. |
 |